Blogs
Recognise, isolate and control
Sep 08,
2023
These three principles are the base of disease control on a mushroom farm. To my opinion there is no farm that has not a spot…
As the sun's warm embrace blankets the earth, a quiet wonder emerges beneath the forest canopies, in fields, and even in our own backyards. Mushrooms,…
Hygiene at the end of the growing cycle
Dec 18,
2023
Lately, several farms have seen some symptoms of virus which means more focus on hygiene is necessary. Hygiene includes all measures aimed at minimizing the…
Exploring the Delightful World of the White Cap Mushroom - A Culinary Adventure by Fred Musc
Jun 07,
2023
Welcome, fellow mushroom enthusiasts! Today, we embark on a fascinating journey into the world of the White Cap mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). Join me as we…
A World of Mushrooms
May 03,
2023
A World of Mushrooms: Where Your Favorite Fungi are Produced Mushrooms are one of the most versatile and nutritious foods on the planet, with a…
A good stagger to meet targets
Mar 27,
2023
The targets for a mushroom farm are amongst others:• Meet market requirements• Good quality at the lowest possible harvesting costsTo meet the market requirements the…
I am losing my quality
Jan 26,
2023
Imagine the third picking day of a first flush. In the morning the pickers are picking a beautiful mushroom. Around noon the mushrooms are starting…
Preserve structure during composting
Nov 15,
2022
Longer pre-wetting of straw to preserve structure during mushroom composting In my 'Pre-wet' blog, I already wrote about the importance of pre-wetting for good mushroom…
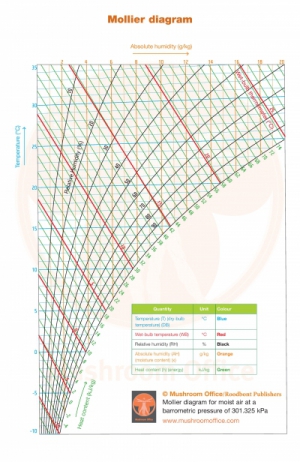
Mollier Diagram
Jun 29,
2022
What is the absolute moisture content of the air? Or the enthalpy of the air? More and more growers have a handy app that reads…